In this article we will talk about common diseases and symptoms of the throat and larynx
Common diseases and symptoms of the throat
1. Pharyngitis:
It is an inflammation of the Pharyngeal mucosa and submucosal tissue. They are divided into acute and chronic pharyngitis. These are primarily caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as hemolytic streptococci, pneumococci, influenza bacteria and viruses. In addition, low human resistance (immunity) is the main internal cause.
Acute pharyngitis: It is an acute inflammation that affects the throat mucosa and submucosa tissue. The main symptoms are initially dryness and burning in the throat, followed by pain. The pain in the throat is often more noticeable when swallowing saliva than when eating. It can be accompanied by fever, headache, loss of appetite and body aches. If it gets into the throat, it can cause hoarseness and coughing.
Chronic pharyngitis: predominantly chronic inflammation of the throat mucosa. Diffuse inflammation is often part of chronic catarrhal inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, often accompanied by inflammation of the pharyngeal lymphoid tissue. It is a common condition that occurs frequently, is relatively persistent and recurrent, and is more common in middle-aged people. The main symptoms are throat discomfort, dryness, itching, swelling, excessive secretion and burning pain, easy choking, foreign body sensation, inability to spit out and difficulty swallowing.
2. Tonsillitis:
Refers to inflammation of the tonsils (also called tonsillitis), usually refers to inflammation of the palatine tonsils, which can be divided into acute and chronic tonsillitis. The main causes of disease are still viruses such as adenoviruses, influenza viruses, parainfluenza viruses, enteroviruses, herpes simplex viruses, etc. In addition, bacteria such as streptococci, mycoplasmas, diphtheria, staphylococci and diphtheria pneumonia can also cause the disease. The inflammation. Acute tonsillitis is contagious; Chronic tonsillitis is often accompanied by multiple and repeated acute attacks, such as: B. high fever, severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing and general tiredness.
Pharyngitis is mainly an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat wall; Tonsillitis is primarily an inflammation of the mucous membrane, crypts, parenchyma, or follicles of the tonsils. Both often exist at the same time and influence each other.
3. Angina pectoris:
This is an acute inflammation that occurs in the isthmus, a special form of pharyngitis. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses and other germs and is contagious. Symptoms include dry throat, foreign body sensation, herpes, ulcers, etc., which are similar to the symptoms of acute tonsillitis.
4. Pharyngeal ulcer: This is a localized defect and ulceration of the surface tissue of the pharyngeal mucosa. The surface is often covered with pus, necrotic tissue or eschar and scarring occurs after incomplete recovery. Most of them are caused by pharyngitis that has not healed for a long time.
Common diseases and symptoms of the throat:
1. Epiglottitis:
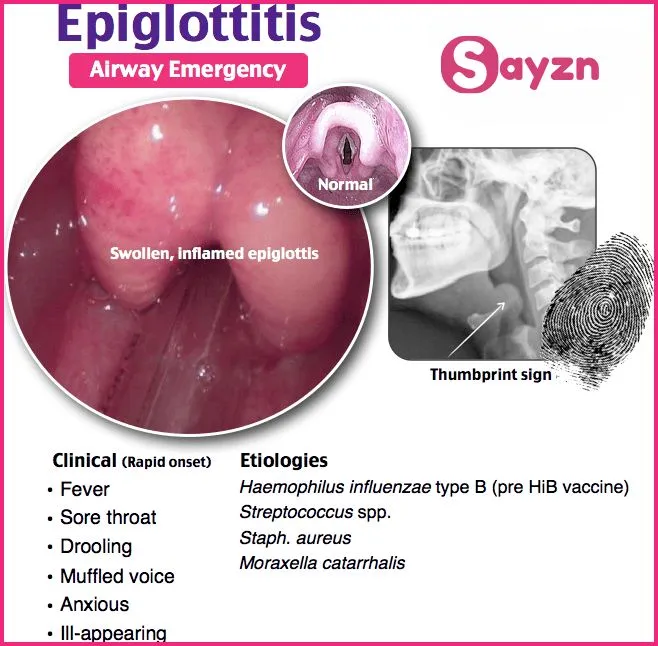
Refers to the swelling of the epiglottis when the mucosal tissue on the cartilage at the entrance to the larynx becomes infected and blocks the airway. Epiglottitis is a potentially fatal infection that affects children ages 2 to 6 and is often caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Symptoms are often acute and explosive. Previously healthy people suddenly develop a sore throat, hoarseness, shortness of breath and high fever and quickly develop respiratory distress characterized by dysphagia, salivation, dyspnea, tachypnea and inspiratory wheezing.
2. Laryngitis:
It is an inflammation of the throat lining caused by a general bacterial infection. Depending on the degree of the disease, it can be divided into chronic simple laryngitis (the larynx mucosa and submucosa tissue are congested, red and swollen, with some lymphocyte infiltration, and the basement membrane is widened and loosened); chronic hypertrophic laryngitis (the epithelium of the larynx mucosa is thickened), with squamous metaplasia and keratinization, significant proliferation of submucosal fibrous tissue and infiltration of a large number of inflammatory cells); chronic atrophic laryngitis (the larynx mucosa is atrophic and thin, dry and shiny, the vocal cords are thinner and the tension is weakened). Hyperplasia of the submucosal fibrous tissue of the larynx, mucosal atrophy and glandular atrophy and disappearance).
Vocal cord nodules are a form of chronic laryngitis. Initially, the nodules are soft and red, the blood vessels are dilated and blocked, and interstitial edema occurs. Later, fibrosis and hyaline degeneration occur, and the superficial epithelial spinous layer becomes thickened and keratinized. This causes it to become firm and pale.
3. Laryngeal closure:
These are a group of syndromes in which lesions in the larynx or adjacent organs narrow the airways in the larynx and cause breathing difficulties. Acute laryngeal obstruction caused by acute inflammation, laryngeal foreign body, laryngeal trauma, allergic edema, bilateral laryngeal nerve paralysis, etc.; caused by consequences of laryngeal trauma, scar hyperplasia caused by iatrogenic surgery and compression of neck lesions, etc., resulting in chronic laryngeal obstruction.
The development and subsequent effects of acute and chronic diseases of the pharynx and larynx. If the metabolism of human tissue cells cannot be adjusted and restored in time, it basically leads to damage to the mucosal epithelial cells and submucosa-related tissues (muscles, blood vessels, nerves, lymphocytes) in the throat and the parts connected to the larynx. etc.) Cell damage, lesions and necrosis have persistent and repeated effects on various subsequent physiological functions of the pharynx and larynx (the pharynx and larynx are at extremely high risk of being invaded by external pathogenic microorganisms).